Anxiety: types, causes, symptoms, and treatment
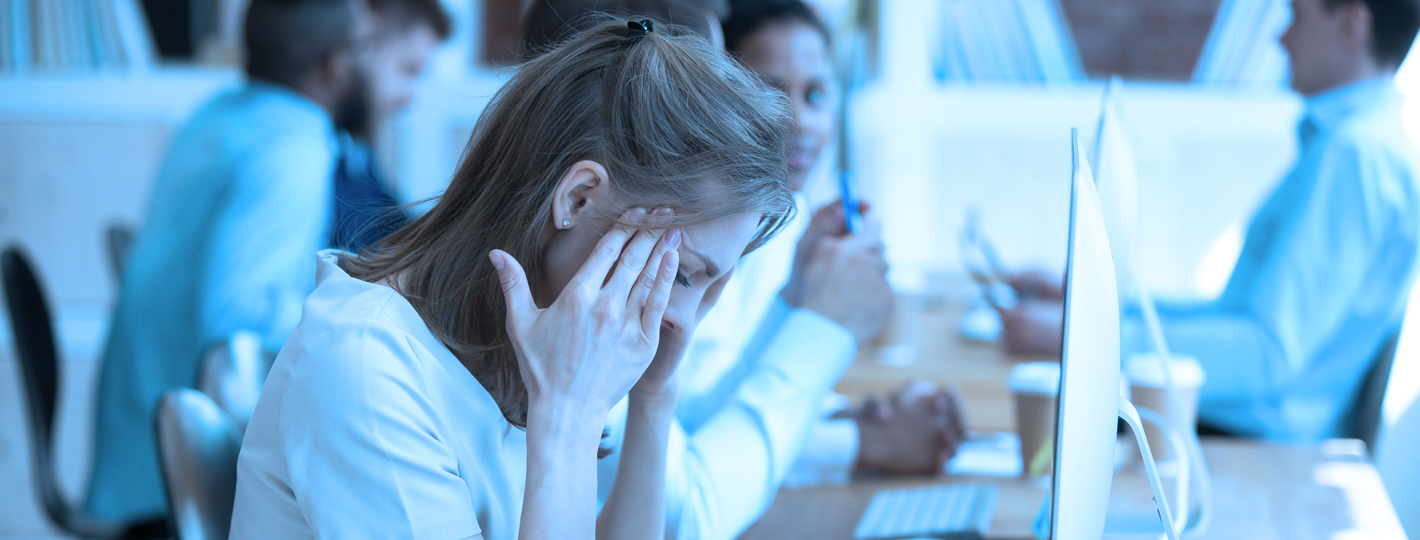

What is anxiety?
A thorough understanding of what anxiety is, the different types of anxiety, and the associated symptoms is essential for identifying and applying the most effective treatment strategies. This awareness helps affected individuals better manage their condition and contributes to reducing the stigma associated with mental health disorders.
Anxiety is a state of fear and unease, characterized by rapid heartbeat, sweating, fatigue, insomnia, and difficulty concentrating. Sometimes, it occurs as a normal reaction to stress, which everyone experiences at certain moments in life.
For example, you may feel anxious when facing a difficult problem at work, before an exam at school, or prior to making an important decision. In such temporary situations, anxiety can provide an extra boost of energy and adrenaline, helping you focus better.
However, the problem arises when anxiety becomes persistent and overwhelming. Individuals may experience physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, or digestive issues, which are often the body’s response to prolonged stress.
Why does anxiety occur and what are its causes?
Anxiety arises as a complex response of the body to various stressful situations or perceived threats, having its roots in both biological factors and environmental influences or life experiences.
The causes of anxiety can be multiple and varied, reflecting an interaction between genetic predisposition, brain chemistry, and psychosocial factors. Understanding the complexity and diversity of these causes is essential for an effective approach and for providing appropriate support to those who struggle with anxiety disorders.

From a biological perspective, anxiety can be caused by an imbalance of neurotransmitters in the brain—chemical substances that play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotions. Serotonin and norepinephrine, for example, are often associated with well-being and emotional balance. If the levels of these neurotransmitters are insufficient, this may contribute to the development of anxiety states and other mental health disorders.
There is also evidence suggesting that anxiety may have a genetic component. You are more likely to experience this condition if a close relative also struggles with it. Moreover, the presence of anxiety disorders among family members may indicate a shared genetic vulnerability.
The way a person perceives and reacts to stress can also influence their susceptibility to anxiety. Individuals with perfectionist tendencies, those who have difficulty managing stress, or who possess anxious personality traits may be more prone to developing anxiety disorders.The way a person perceives and reacts to stress can also influence their susceptibility to anxiety. Individuals with perfectionist tendencies, those who have difficulty managing stress, or who possess anxious personality traits may be more prone to developing anxiety disorders.
Life experiences can also be causes of anxiety. Childhood trauma, abuse of any kind, the loss of a loved one, or extremely stressful experiences can trigger or worsen anxiety states. Difficult life situations such as financial problems, relationship conflicts, or workplace stress are also significant factors that may contribute to the onset of anxiety.
When discussing the causes of anxiety, it is important to take a look at daily habits and lifestyle. These can have a major impact on overall well-being and emotional health. Excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, lack of physical activity, or irregular sleep patterns can intensify anxiety symptoms.
What are the symptoms of anxiety?
The symptoms of anxiety can vary significantly from one person to another, depending on the type of anxiety experienced as well as individual characteristics. People who suffer from anxiety disorders may experience excessive fear or worry related to a specific situation or to a wide range of everyday situations. Usually, these individuals face anxiety symptoms over a long period of time—at least several months.
It is important to note that anxiety manifests through both physical and emotional symptoms, affecting an individual’s life in a complex way. Below is a comprehensive list of common symptoms associated with anxiety:
- Restlessness or inner tension: a constant feeling of being “on edge,” difficulty relaxing
- Excessive worry: persistent and often irrational concerns about everyday events or activities
- Intense fear or panic: sudden panic attacks accompanied by overwhelming fear, without an obvious cause
- Difficulty concentrating: inability to focus on tasks or maintain attention
- Irritability: a tendency to become easily frustrated or annoyed
- Palpitations or rapid heartbeat: the sensation that the heart is beating too fast, irregularly, or forcefully
- Sweating: cold chills or excessive sweating without physical exertion or high temperatures
- Trembling or muscle spasms: uncontrollable shaking sensations
- Rapid breathing or shortness of breath: feelings of suffocation or inability to breathe properly
- Numbness or tingling sensations: in the hands, feet, or other parts of the body
- Headaches, neck or shoulder tension: frequent pain in these areas, often linked to muscle tension
- Digestive problems: abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, constipation, or other gastrointestinal issues
- Fatigue: persistent feelings of exhaustion or lack of energy
- Insomnia: difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, frequent awakenings during the night
What types of anxiety exist?
When it comes to anxiety, its broad spectrum includes several types and subtypes, each with specific characteristics and patterns of manifestation. Recognizing and understanding the different types of anxiety is essential in order to provide the most appropriate and effective therapeutic approach.
Below is an overview of the most common types of anxiety:
Diagnosis and treatment of anxiety
The diagnosis and treatment of anxiety involve a series of specific steps designed to identify the type and severity of the disorder, the causes behind the onset of anxiety, and to provide the most appropriate remedy for recovery. The diagnostic and treatment process may vary depending on each individual’s needs.
The diagnosis of anxiety disorders often begins with a thorough evaluation conducted by a mental health professional. This may include:

- Clinical interview: a detailed discussion about the experienced symptoms, medical and family history, as well as the impact of anxiety symptoms on daily functioning.
- Questionnaires or assessment scales: standardized tools that help measure the severity and type of anxiety.
- Medical examinations: used to rule out other medical conditions that may contribute to anxiety symptoms, such as thyroid disorders or nutritional deficiencies


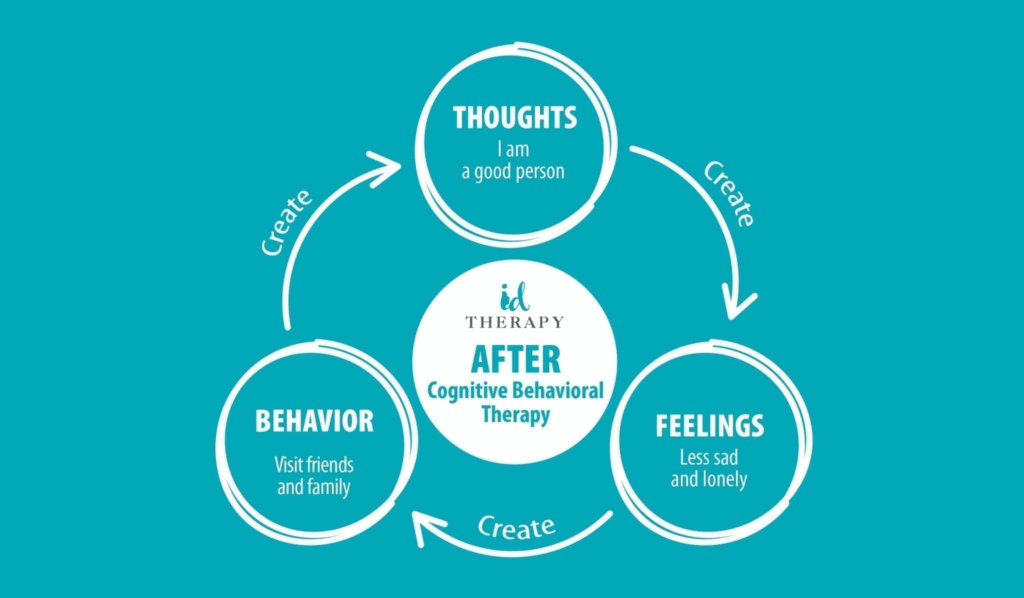



Virtual Reality Psychotherapy
One of the most innovative therapeutic approaches for treating anxiety and panic attacks is Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET). This method uses virtual reality technology to provide therapeutic solutions for a wide range of conditions.

Buspirone: an anxiolytic option that is not part of the benzodiazepine class and carries a lower risk of dependence. It is often used for long-term management of generalized anxiety.
Beta-blockers: such as propranolol, are sometimes prescribed to control physical symptoms of anxiety (e.g., palpitations or tremors) in specific situations, such as before public speaking.
- Regular physical exercise: helps reduce tension and improve overall well-being.
- Stress management techniques: incorporating mindfulness and yoga into daily routines can be beneficial.
- Avoiding stimulants: reducing or eliminating caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine can lessen anxiety symptoms.


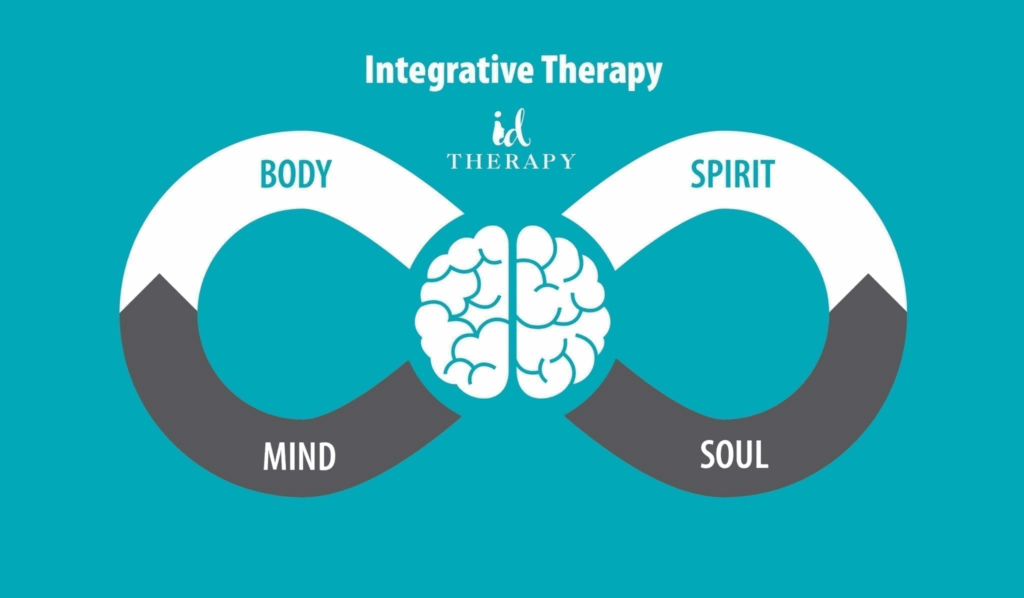
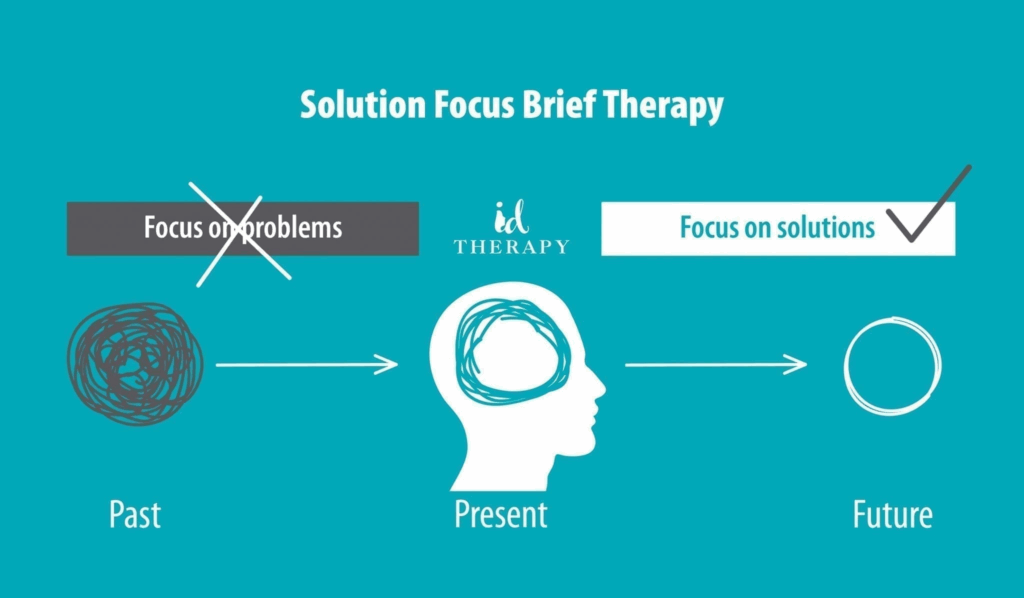


Prevention and recommendations for managing anxiety states
Maintain a balanced diet: Healthy nutrition can positively influence mood and energy levels. Avoid excessive caffeine and sugar, which can intensify anxiety symptoms.
Regular physical exercise: Physical activity releases endorphins, improving overall well-being and helping manage stress.
Adequate rest: Sufficient, high-quality sleep is crucial for mental health. Try to maintain a regular sleep schedule.
Limit alcohol and nicotine consumption: Substances that may initially seem relaxing can actually worsen anxiety in the long term.
Deep breathing exercises: Breathing techniques can help calm the nervous system and reduce anxiety symptoms.
Mindfulness and meditation: These practices improve present-moment awareness and reduce the tendency to worry about the future.
Progressive muscle relaxation: Alternating tension and relaxation in different muscle groups can reduce physical and mental stress.
Time management: Efficient organization can reduce feelings of being overwhelmed and help prevent procrastination.
Setting realistic goals: Break large tasks into small, manageable steps to avoid overload.
Open communication with friends and family: Having a support network can provide comfort and encouragement during difficult times.
Counseling or therapy: A mental health professional can offer personalized strategies for managing anxiety.
Support groups: Sharing experiences with others who face anxiety can be comforting and provide new perspectives.
Experience advanced neuromodulation
Free yourself from stress and anxiety – breathing exercises
Adress: Naum Ramniceanu Street, no. 23, ap. 1, Sector 1, Bucharest, Romania
