Schizophrenia
What Is Schizophrenia: Causes, Types, Symptoms, Treatment
What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder related to psychosis, characterized by impaired thought processes, inappropriate emotional responses, and a loss of vital contact with reality. This condition mainly affects adolescents and adults under the age of 40–45, with a global lifetime prevalence of approximately 0.3–0.7%.
The onset of schizophrenia in men may occur around the age of 20, while in women it usually begins around the age of 30. In children and adults over the age of 45, onset is extremely rare.
The onset of schizophrenia is gradual, with subtle symptoms at first that may progress over time. It is a complex condition, with a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors contributing to its development.
People with schizophrenia may experience hallucinations (voices or images that are not real), delusions (false beliefs), disorganized thinking, and abnormal motor behavior. This disorder profoundly affects a person’s daily life, influencing their ability to function normally in society and maintain interpersonal relationships.
Schizophrenia manifests through a mental dissociation accompanied by a chaotic invasion of imagination, leading to the appearance of major psychopathological manifestations. These include hallucinations, delusions, formal thought disorders, affective disorders, behavioral disorders, and personality disorganization.
It is important to note that schizophrenia is one of the most severe psychiatric disorders, with serious consequences both for those affected and for their families. In addition, the course of the disease is unpredictable, even despite modern treatments that have significantly improved the prospects for social reintegration of people with schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia usually appears in late adolescence or early adulthood, but it can also occur later.
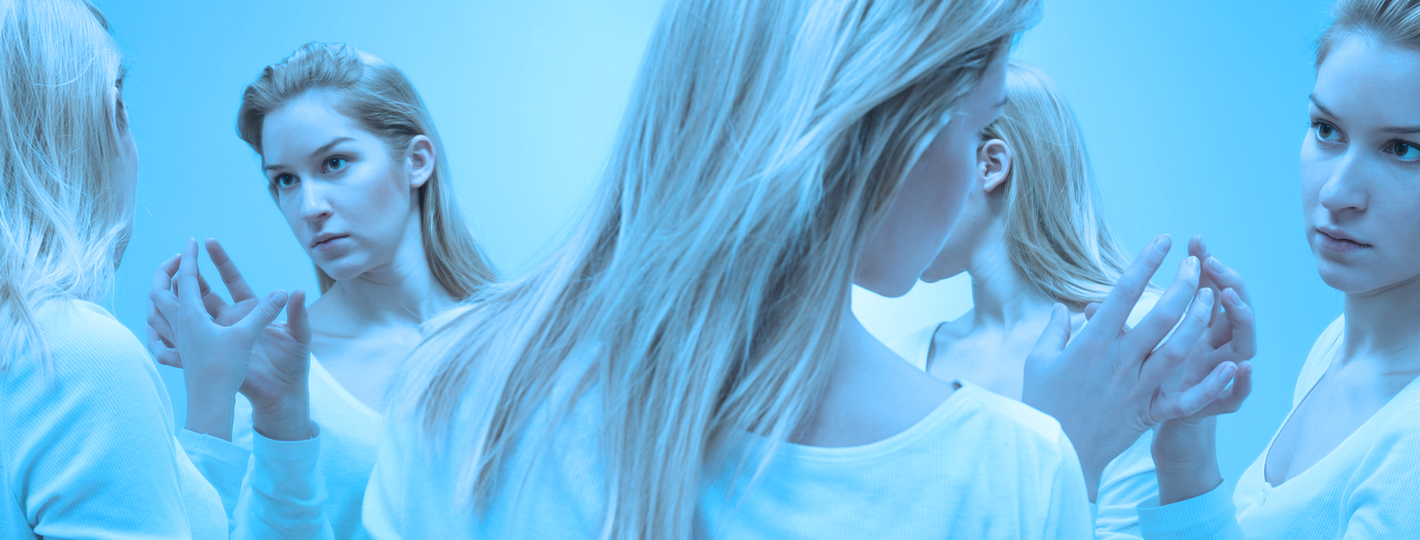

What are the causes of schizophrenia?
Genetic factors
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of schizophrenia. If you have a family member with schizophrenia, your risk of developing this disorder increases considerably. Genes involved in brain function and neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate may influence risk.
Biological factors
Chemical imbalances in the brain, especially involving the neurotransmitters mentioned above, are essential to understanding schizophrenia. Structural and functional brain abnormalities, such as enlarged cerebral ventricles or abnormal activity in certain brain regions, may also contribute to the onset of symptoms.
Chronic stress
Stressful life events and trauma can contribute to triggering schizophrenia.
Malnutrition and viral infections during intrauterine life
Prenatal factors, such as inadequate nutrition or viral infections during pregnancy, can increase the risk of schizophrenia in the child.
How many types of schizophrenia are there?
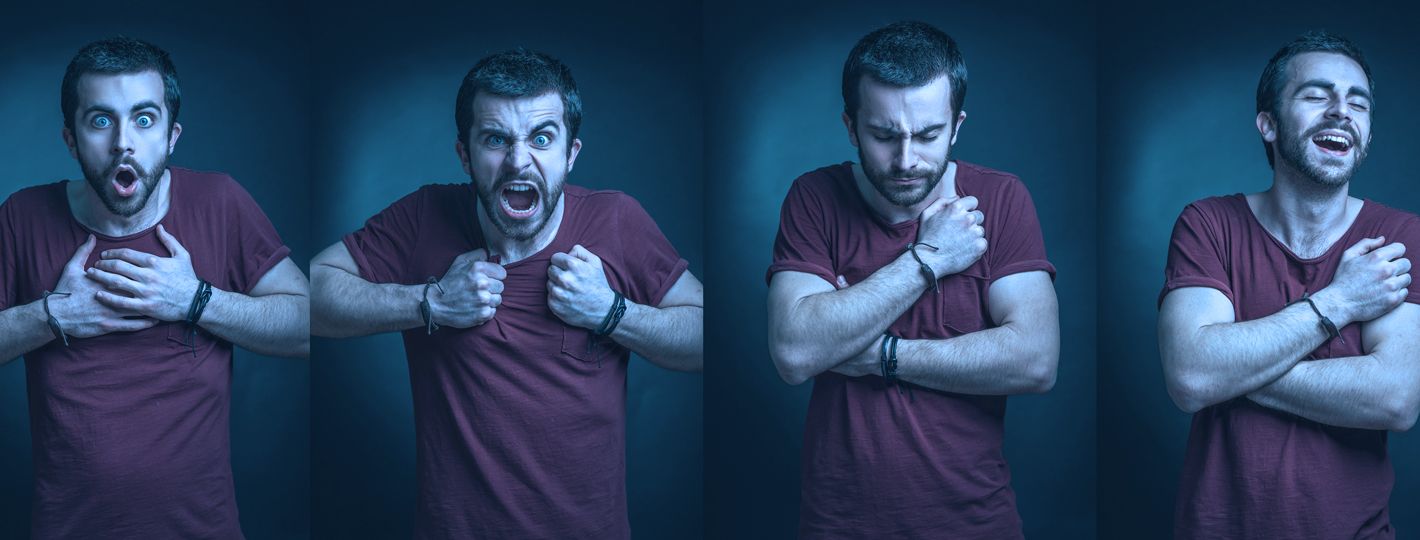

What are the early signs of the onset of schizophrenia?
- Behavioral and emotional changes: The person may become withdrawn, avoiding friends and activities they previously enjoyed. Anxiety and suspicion increase, and thoughts become disorganized.
- Difficulties with concentration and decreased performance: At work or school, people with schizophrenia may notice a sudden decline in performance due to difficulties concentrating and organizing thoughts. Ordinary tasks become challenging; for example, a previously successful student may struggle to complete assignments or stay focused during classes.
- Hallucinations and delusions: These symptoms severely distort reality. Hallucinations often involve hearing nonexistent voices that give commands or comment on behavior. Delusions involve false beliefs, such as being followed or possessing supernatural powers, which can lead to extreme suspicion or inappropriate actions.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
- Hallucinations: The person may hear voices or see things that are not real. For example, a person may hear a voice giving commands or see people and objects that do not exist.
- Mystical delusions: Individuals have false beliefs, such as the idea that someone is plotting against them, that they are being constantly followed, or that they possess special, supernatural powers.
- Disorganized thinking: This manifests as incoherent speech and significant difficulties in organizing thoughts. For example, a person may jump from one topic to another without any logical connection.
- Abnormal motor behavior: Individuals display repetitive movements or agitated behavior, such as nervous tics or strange, meaningless physical movements.
- Lack of motivation: This is manifested through difficulties in initiating and sustaining daily activities. For example, a person may struggle to find the energy to get out of bed or to complete everyday tasks.
- Social withdrawal: Avoiding social interactions and isolating oneself leads to social withdrawal. The person may avoid talking to friends or family and prefer to stay alone.
- Flat affect: This symptom indicates a lack of emotional expression. For example, the person may seem to have no emotional reactions, even in situations that would normally provoke joy or sadness.
- Functional difficulties: A person may struggle with ordinary tasks, such as self-care or caring for loved ones. This often results in neglecting personal hygiene or having trouble keeping their living environment clean.
The Impact of Technology in Schizophrenia
- Technological benefits: Technology offers numerous tools that can help manage schizophrenia. Mental health monitoring apps allow patients to track their symptoms and adjust their treatment in real time, while online support groups provide a safe space to share experiences and find support.
- Technological challenges: Excessive use of social media can worsen symptoms. Exposure to misinformation, cyberbullying, and sensory overload can intensify hallucinations and paranoia. Digital overload may also lead to social isolation and the deterioration of mental health.
- Responsible use: It is essential for people with schizophrenia to use technology in a balanced way. Professional support combined with a mindful digital routine can contribute to better symptom management and an improved quality of life.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed?
- Initial evaluation: The first step in diagnosing schizophrenia is a detailed discussion with a mental health specialist. They will investigate the symptoms, medical and family history, as well as the patient’s daily behavior.
- Physical examination: After the initial evaluation, a physical examination is performed to rule out other medical conditions that might cause similar symptoms. This may include blood tests, brain imaging (MRI or CT), and other laboratory analyses.
- Psychological evaluation: Questionnaires and structured interviews are used to assess the patient’s emotional and mental state. These tools help identify the presence and severity of hallucinations, delusions, and other cognitive symptoms.
- DSM-5 criteria: An official diagnosis is based on the criteria set by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which specifies the exact symptom duration and type required for a schizophrenia diagnosis.
- Long-term monitoring: To ensure an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan, long-term monitoring of symptom evolution and treatment response is necessary to adjust care as needed.

How Can Schizophrenia Be Treated?
- Antipsychotic medication: The first step in treating schizophrenia consists of antipsychotic medications. These help reduce positive symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions. Examples include olanzapine and risperidone.
- Psychosocial therapy: In addition to medication, psychosocial therapy is crucial. This type of therapy helps patients develop life skills, manage stress, and improve interpersonal relationships.
- Family support and education: Involving the family in treatment and educating them about schizophrenia can significantly improve outcomes. Emotional support and understanding from loved ones are essential.
- Modern schizophrenia treatment: Modern treatment methods include innovative approaches such as virtual reality therapy and brain stimulation techniques, which can help manage symptoms and improve daily functioning.
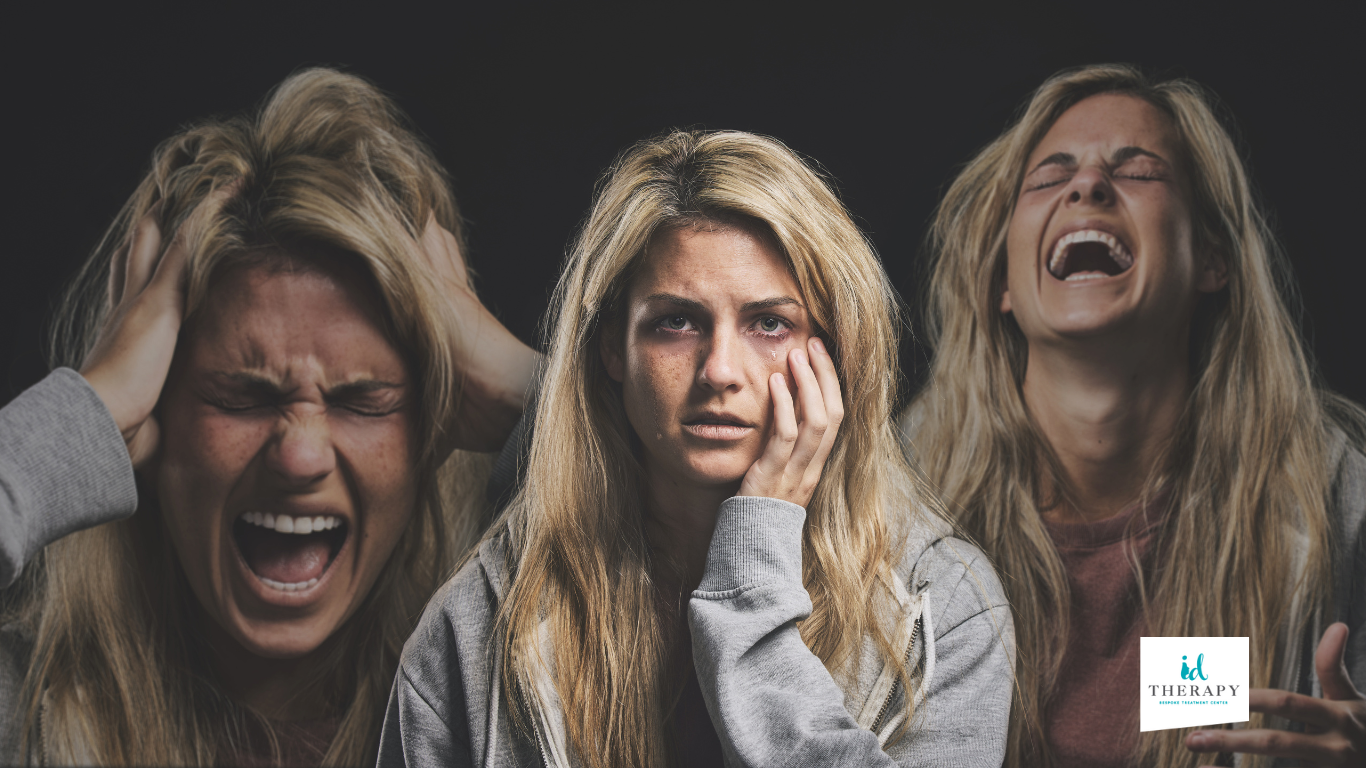

What Complications May Occur If Schizophrenia Is Not Treated?
- Social isolation and withdrawal: Affected individuals may become increasingly withdrawn and isolated, avoiding contact with family and friends as the illness progresses.
- Financial and professional problems: Untreated schizophrenia can lead to significant difficulties maintaining a job or career, often resulting in long-term financial instability.
- Poor physical health: Due to neglecting personal care, patients may develop secondary health problems, including malnutrition and various chronic diseases.
- Dangerous and suicidal behavior: Without proper treatment, there is an increased risk of self-harm and suicide. Hallucinations or delusions—such as hearing voices commanding self-harm or believing one must protect themselves from nonexistent dangers—can lead to impulsive acts. These situations require immediate intervention.
- Legal difficulties: Disorganized or impulsive behavior associated with untreated symptoms can lead to legal complications. Early recognition and professional help are crucial for preventing these outcomes.
- Ensuring a safe environment: Safety must be a priority as a crisis can occur unexpectedly. It is highly recommended that individuals with schizophrenia do not live alone due to the risk of self-harm. Ideally, they should live with informed family members or under the care of a specialist.
How to react during a schizophrenic episode?
- Calm and understanding: Remember that the patient is experiencing a psychotic episode, and direct communication may be difficult. Stay calm and show understanding.
- Avoid irritation: The person may be frightened by their own loss of control, so avoid expressing irritation or anger.
- No shouting or sarcasm: Do not shout and do not use sarcasm, as these can easily worsen the situation and increase the patient’s agitation.
- Minimizing distractions: Reduce environmental distractions such as television, radio, or bright lights to a minimum to help the patient feel less overwhelmed.
- Avoid eye contact and touching: Avoid prolonged eye contact and physical contact. These can be perceived as threatening or invasive during a crisis.
- Sit down: Sit down and invite the patient to do the same to help create a calm, non-threatening environment.
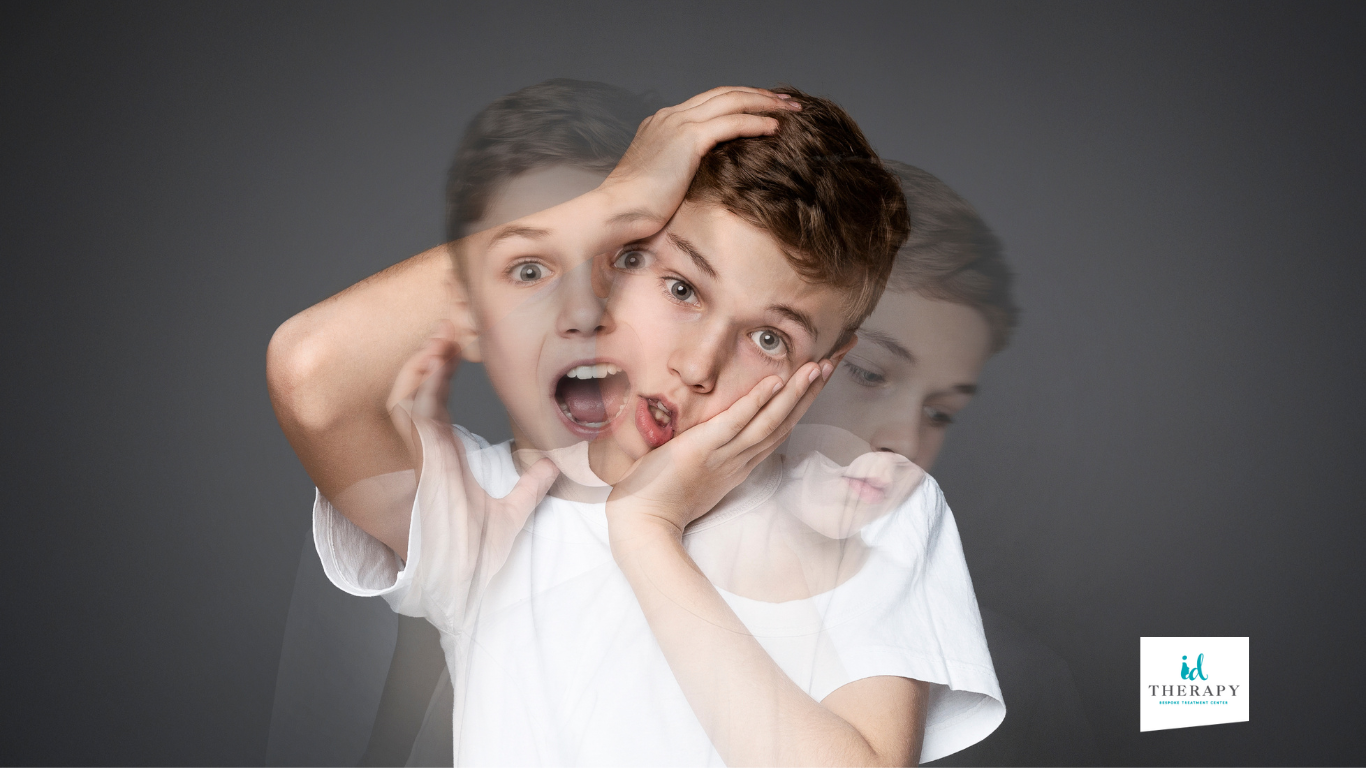

How does schizophrenia manifest in children?
How can schizophrenia be prevented?
- Monitoring risk factors: If you have a family history of schizophrenia, careful monitoring of mental health can help with early identification of symptoms. Regular consultations with a mental health specialist are essential for proactive care.
- Stress management: Stress is a common trigger for many mental disorders. Stress-reduction practices such as meditation, yoga, and regular physical exercise can help maintain overall mental health and stability.
- Avoiding substance use: The use of recreational drugs and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen or trigger schizophrenia symptoms. Avoiding these substances is a critical step in reducing the risk of a psychotic episode.
- Education and family support: Learning about schizophrenia and involving the family in emotional and psychological support can prevent symptoms from worsening and promote early intervention.

How can ID Therapy Clinic help in the treatment of schizophrenia?
Therefore, schizophrenia is a complex and challenging disorder, but with the right support, life can return to a normal course. Early identification, appropriate treatment, and continuous support are essential for managing this condition. You do not have to face this battle alone.
If you or a loved one is dealing with schizophrenia, do not hesitate to seek professional help. Change begins with a first step.
Treating schizophrenia requires a multidisciplinary team consisting of a psychiatrist, a psychologist with expertise in psychosis therapy, and a social worker. Family support is essential for patients diagnosed with schizophrenia, offering them the unconditional love and support they need.
At ID Therapy, we are here to provide the necessary help to people facing schizophrenia. Our team of specialists is ready to help you manage this disorder and regain control over your life. Contact us to begin the recovery process.
Adress: Naum Ramniceanu Street, no. 23, ap. 1, Sector 1, Bucharest, Romania
