Addictions
What Is Alcohol Addiction: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
What is alcohol addiction?
- A woman who consumes more than 7 alcoholic drinks per week or more than 3 drinks within 2 hours;
- A man who consumes more than 14 alcoholic drinks per week or more than 4 drinks within 2 hours.
Causes and risk factors of alcohol addiction
Psychological factors: Many individuals turn to alcohol to manage stress, anxiety, or depression. Alcohol is often used as a coping mechanism to deal with emotional problems or psychological disorders.
Social and cultural influences: Peer pressure and cultural norms that promote alcohol consumption can play an important role in the development of alcoholism. In some cultures or social groups, excessive drinking may be seen as an accepted or even encouraged form of socialization.
Trauma and stress: Traumatic experiences, such as physical or emotional abuse, can contribute to the development of alcohol addiction. Chronic stress in personal or professional life may also lead individuals to use alcohol as a way to escape their problems.
Behavioral modeling: Children raised in environments where alcohol consumption is frequent and normalized may learn to adopt similar behaviors to relax and escape daily life.
Alcohol accessibility: The ease of obtaining alcohol in stores and its low cost can facilitate the development of addiction in individuals predisposed to substance abuse.
Recognizing these factors can help identify individuals at risk and support the implementation of effective prevention and treatment strategies. Treating alcoholism often requires a personalized approach that considers the specific causes and context of each individual.

Symptoms of alcohol addiction
- Regular and excessive alcohol consumption, even in dangerous situations (e.g., driving under the influence).
- Neglecting responsibilities at work and home.
- Continuing to drink despite personal or social problems caused by alcohol.
- Reducing or abandoning social activities and hobbies.
- Repeated but unsuccessful attempts to reduce or control alcohol intake.
- Development of alcohol tolerance, requiring increased amounts to achieve the same effects.
- Withdrawal symptoms when alcohol is not consumed, such as tremors, sweating, nausea, insomnia, agitation, anxiety, and even hallucinations or severe seizures.
- Recurrent physical problems associated with excessive alcohol consumption, such as liver disease, gastrointestinal issues, and heart problems.
- Anxiety and depressive episodes.
- Decreased judgment and decision-making ability, affecting work performance and other areas of life.
- Mood changes, increased irritability, and aggressive behavior.
Diagnosis of alcoholism – Identifying the signs of addiction
How ID Therapy Clinic can help treat alcohol addiction
Clinical interviews: During consultations, physicians or psychiatrists use detailed interviews and questionnaires to assess alcohol consumption and its impact on the patient’s life. These tools help determine the frequency of drinking, the amount consumed, and the behavioral effects associated with addiction.
Observation of physical and behavioral symptoms: Physical signs of alcoholism include the smell of alcohol on the breath, hand tremors, facial flushing, bloodshot eyes, agitation, and sweating. From a behavioral perspective, the doctor and therapist will look for indicators such as neglecting responsibilities, drinking in dangerous situations, and the inability to reduce or control alcohol consumption.
Assessment of social and personal impact: Professionals will examine how alcohol use affects interpersonal relationships, work performance, and other aspects of the individual’s social and personal life. Loss of interest in hobbies and activities that were previously enjoyable, as well as social isolation, are important diagnostic signals.
Medical tests: Blood tests may be performed to check liver enzyme levels (which may indicate liver damage) and other parameters related to chronic alcohol use. Tests may also be used to detect the presence of alcohol in the blood.
Early recognition of the signs of addiction and seeking specialized help are essential for the effective treatment of alcoholism. Treatment may include psychological therapy, medication, group support, and other interventions to help individuals manage addiction and regain control over their lives.


What effects does alcohol addiction have on the body?
Treatment for alcohol addiction
Detoxification: This is carried out under medical supervision in a controlled environment. It helps the individual safely eliminate alcohol from the body, with medical management of withdrawal symptoms, which can sometimes be severe and even life-threatening.
How ID Therapy Clinic can help treat alcohol addiction

The patient is placed in various virtual environments (bar, restaurant, shop, party, or at home) where specific trigger cues are present that may tempt them to consume alcohol or nicotine. The therapist helps the patient identify the physical and cognitive symptoms of the craving they experience. The patient is also guided to develop new behaviors or cognitive strategies for avoidance, distraction from trigger cues, self-talk, and changing thinking patterns. Certain alcoholic beverages preferred by the patient can be placed by the therapist within these virtual environments. In addition, a virtual bartender provides opportunities for the patient to engage in interactions and strengthen their abstinence or moderation skills.
Specific psychotherapy types offered by ID Therapy Clinic


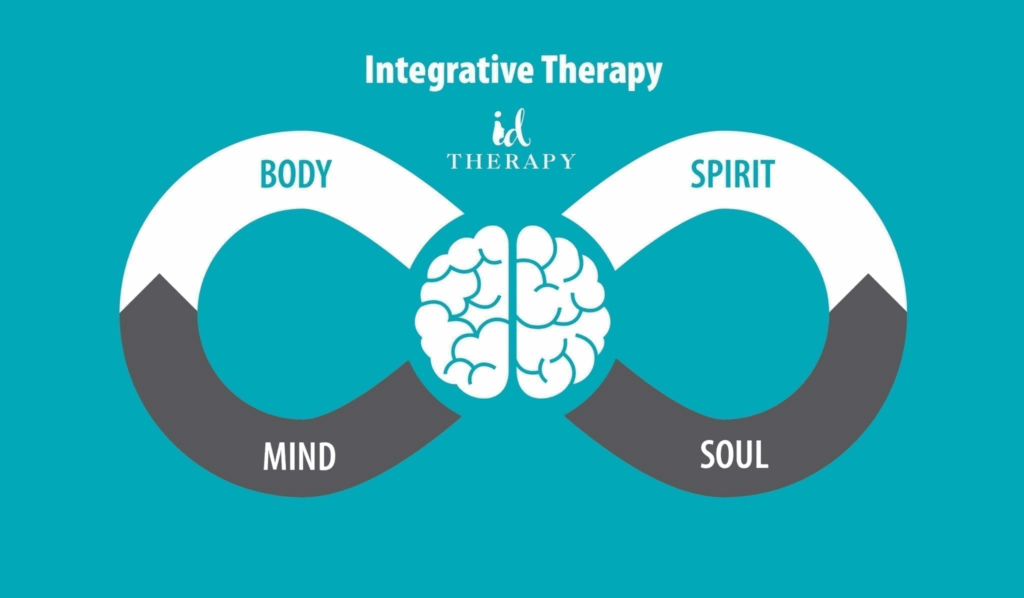
A more flexible and comprehensive approach compared to traditional psychotherapies. A progressive form of psychotherapy, personalized to the individual.
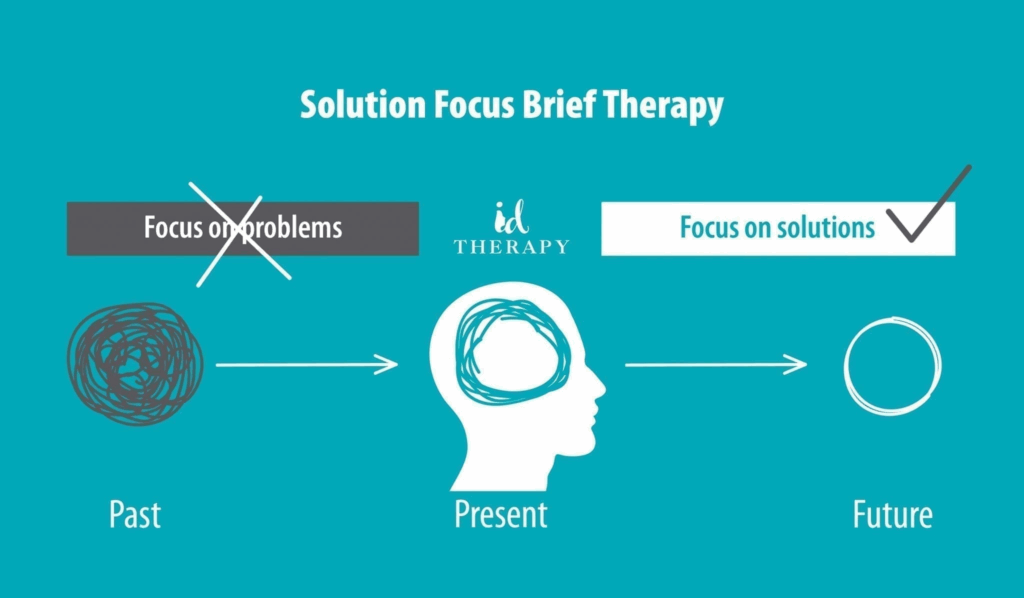
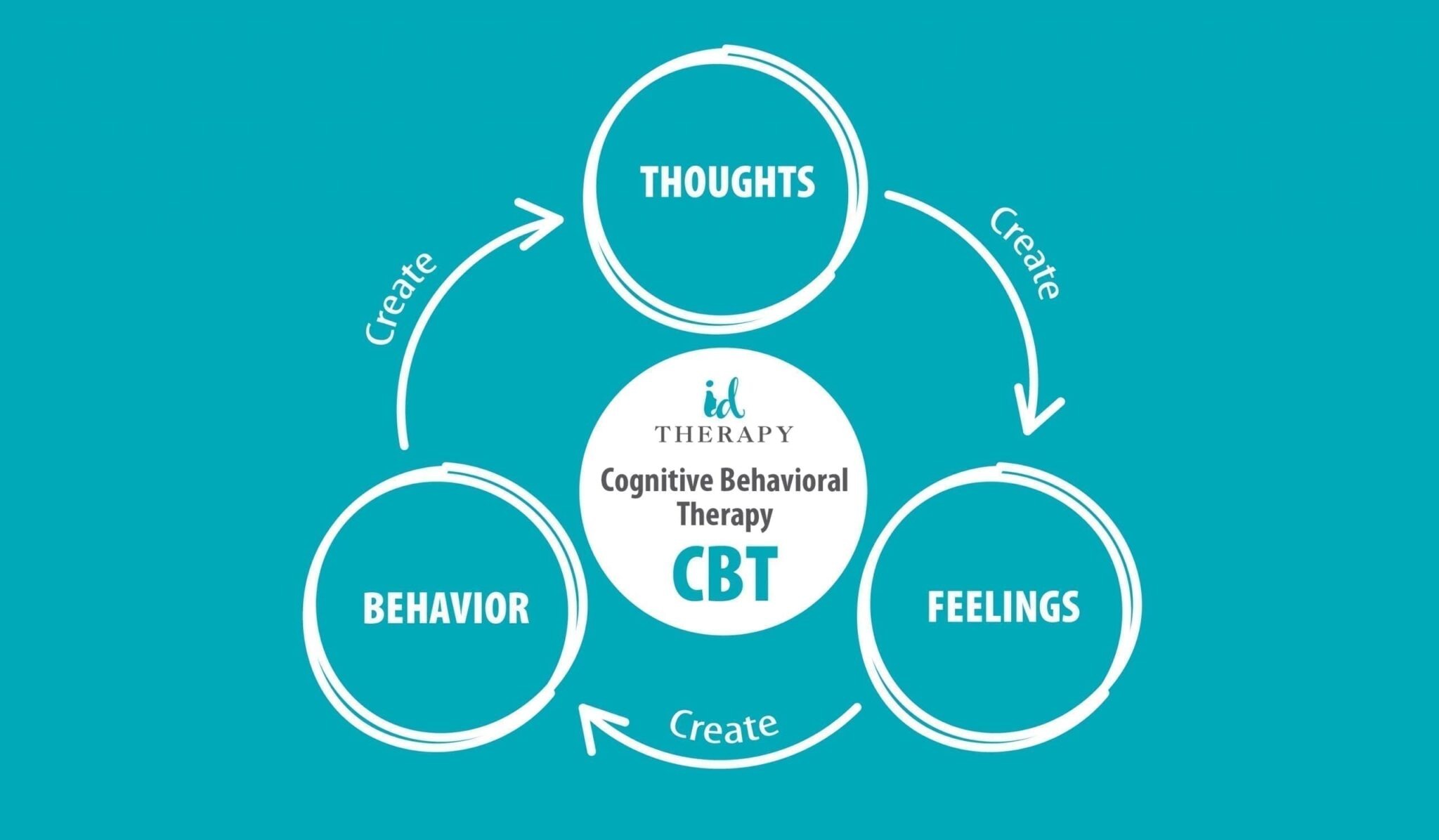

Safe amount of alcohol you can consume
The safe amount of alcohol a person can consume depends on several factors, including age, sex, overall health status, and family history related to alcohol problems. It is also important to note that “safe” does not necessarily mean risk-free, but rather a level at which the risks of developing short- or long-term health problems are reduced.
In many countries, recommended consumption limits are expressed in alcohol units, where one standard unit of alcohol contains approximately 10 grams of pure alcohol. This is roughly the amount of alcohol found in a small glass of wine, a standard-sized beer, or a small serving of spirits.
- For men: no more than 2 units of alcohol per day and no more than 14 units per week.
- For women: no more than 1 unit of alcohol per day and no more than 7 units per week.
Experience advanced neuromodulation
Free yourself from stress and anxiety – breathing exercises
Tips for preventing alcohol addiction or alcoholism
- Know your limits: It is important to be aware of how much alcohol you consume and to respect the recommended limits for moderate drinking.
- Alcohol-free days: Include days in your routine when you do not consume alcohol at all. This can help prevent the development of dependence and allows the body to recover.
- Avoid using alcohol as “medicine”: Do not use alcohol as a way to manage stress, anxiety, or depression. Instead, seek healthy coping methods such as physical exercise, meditation, hobbies, or talking with a therapist.
- Be mindful of family history: If there is a history of alcoholism in your family, you are at a higher risk of developing dependence. Being aware of this risk allows you to take proactive steps to limit alcohol consumption.
- Engage in alcohol-free activities: Participate in social activities that do not revolve around alcohol consumption.
- Education: Learn about the risks associated with excessive alcohol use. Understanding the negative effects on physical health can serve as a strong deterrent.
- Support: When alcohol consumption becomes problematic, seek help. There are many available resources, including counseling, support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous, and treatment programs.
- Create a supportive environment: A supportive environment, such as close family and friends, can reduce social pressure and provide encouragement during difficult times.
Adress: Naum Ramniceanu Street, no. 23, ap. 1, Sector 1, Bucharest, Romania
