Stress
What Is Stress: Causes, Symptoms, Types, Treatment, Prevention
Discover what stress is, its causes, and how many types of stress exist. Learn about common stress symptoms, as well as treatment and prevention methods.
What Is Stress?
The body responds to stress by releasing hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which prepare the body to deal with the perceived threat. This response is known as the “fight or flight” response. While this reaction can be beneficial in the short term, prolonged stress can lead to various health problems, including sleep disorders, digestive issues, high blood pressure, and even heart disease.
Stress is an inevitable part of modern life, but understanding its causes and symptoms can help identify effective ways to manage it and minimize its impact on overall health and well-being.
What Are the Causes of Stress?
Workplace Problems
One of the main causes of stress is related to the work environment. Tight deadlines, heavy workloads, and high expectations can lead to chronic stress. Conflicts with colleagues or supervisors, lack of control over tasks, and job insecurity are additional factors that contribute to work-related stress.
Financial Problems
Financial stress is another major cause of stress. High debt, unexpected expenses, job loss, or insufficient income to cover daily needs can cause constant anxiety and worry. Global economic uncertainty can further intensify this type of stress.
Health Problems
Poor health or the diagnosis of a serious illness is a significant source of stress. Caring for a sick loved one can also add an extra layer of stress. Fear of pain, medical costs, and the impact on quality of life are major stressors in this context.
Interpersonal Relationships
Conflicts in personal relationships—whether with a life partner, family members, or friends—can generate considerable stress. Lack of emotional support, poor communication, and unrealistic expectations contribute to tension and stress. Life events such as divorce or the loss of a loved one are extremely stressful.
Major Life Changes
Any significant life change can be a source of stress. This includes events such as moving to a new home, changing jobs, getting married, having a child, or even retirement. Even positive changes can generate stress due to the need to adapt to new circumstances.
Environmental Factors
The surrounding environment plays an important role in causing stress. Pollution, noise, overcrowding, and poor living conditions can increase stress levels. Natural events such as natural disasters can also cause acute stress.
Psychological and Emotional Issues
Anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders are internal causes of stress. Managing these conditions often requires professional support, and lack of such support can exacerbate stress. Perfectionism and low self-esteem are additional contributors to psychological stress.

What Symptoms Are Specific to Stress?
1. Physical Symptoms of Stress
- Headaches: Tension and stress can cause frequent headaches and migraines.
- Digestive problems: Stress can lead to digestive issues such as stomach pain, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Muscle tension: Many people experience muscle tension and pain, especially in the neck, shoulders, and back.
- Chronic fatigue: Constant stress can lead to chronic fatigue, even without significant physical exertion.
- Sleep problems: Insomnia or unrefreshing sleep is common among people experiencing stress.
- Increased heart rate: A rapid heartbeat or palpitations are signs of intense stress.
2. Emotional Symptoms of Stress
- Anxiety: Stressed individuals may feel constantly worried, even without a clear reason.
- Irritability: Stress can lead to irritability and anger outbursts over minor issues.
- Depression: Prolonged stress may contribute to the development of depression, characterized by deep sadness and loss of interest in daily activities.
- Feeling overwhelmed: People under stress often feel unable to cope with daily responsibilities.
- Social withdrawal: Stress may cause individuals to avoid social contact and isolate themselves from friends and family.
3. Cognitive Symptoms of Stress
- Difficulty concentrating: Trouble focusing on tasks or maintaining attention.
- Poor memory: Stress can impair short-term memory and information retention.
- Poor decision-making: Stress can interfere with clear and rational decision-making, leading to impulsive or incorrect choices.
Repetitive thoughts: Obsessive or repetitive thoughts about ongoing problems.
4. Symptoms of Severe Stress
- Panic attacks: Extreme stress can trigger panic attacks, characterized by shortness of breath, palpitations, and intense fear.
- Eating disorders: Severe stress may cause drastic changes in appetite, including overeating or loss of appetite.
- Cardiovascular problems: Prolonged stress can contribute to serious health conditions such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Weakened immune system: People exposed to intense stress are more susceptible to infections due to a compromised immune system.
Chronic pain: Severe stress can intensify chronic pain and worsen pre-existing conditions.
How Many Types of Stress Exist?
Stress can be classified into several types, depending on its duration and nature. Understanding these types helps identify stress sources and how they affect our lives. The most common types of stress include:
Acute stress is the most common type of stress and occurs in response to immediate demands and pressures. It is usually short-term and can be caused by specific events.
For example, imagine you have a tight deadline at work to complete an important project. You feel intense pressure as the deadline approaches, but the stress significantly decreases once the project is completed.
This type of stress occurs when a person frequently experiences episodes of acute stress. People who lead hectic lives filled with recurring crises usually experience this type of stress.
An example is a person who constantly juggles the demands of a stressful job, family responsibilities, and other social commitments, experiencing frequent stress episodes every week.
Chronic stress is a prolonged form of stress that occurs when a person faces long-term stressful situations. This type of stress can lead to serious health problems.
If you are in an abusive relationship or a toxic work environment, you may experience continuous and persistent stress with no apparent long-term solution.
Traumatic stress occurs in response to a major traumatic event and is often associated with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). The traumatic event can be so severe that it leaves deep psychological scars on the affected person.
For example, surviving a serious car accident in which the person experienced or witnessed severe injuries or death can lead to intense and persistent stress related to the trauma of the event.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a psychiatric condition that may occur after exposure to a severe traumatic event. It is characterized by symptoms that persist long after the initial event.
For instance, a survivor of a terrorist attack who witnessed extreme violence and loss of life may experience flashbacks, nightmares, hypervigilance, and avoidance of places or situations that remind them of the attack, experiencing significant difficulty in resuming a normal life.
Developmental stress occurs as a result of normal life transitions that require adaptation and change. Although natural, these transitions can be stressful as individuals adjust to new circumstances.
An example is the transition from school to university, where a young person must adapt to a new environment, make new friends, and face higher academic demands.
Occupational stress is associated with the workplace and can result from excessive job demands, lack of control over work, or conflicts in the workplace.
An employee who must manage multiple projects simultaneously, without sufficient resources and under constant pressure from strict deadlines, experiences a high level of occupational stress.
This type of stress occurs when there are conflicts between the different roles a person must fulfill in their life, whether at work or in their personal life.
A full-time working mother who must also manage household and parenting responsibilities may experience role stress due to conflicting demands and lack of time to manage everything effectively.
What Effects Does Stress Have on Health?
Stress has numerous negative effects on human health, both physically and psychologically. Understanding these effects is essential for effectively addressing and managing stress.
There are two main categories of stress-related health effects:
- Physical Effects of Stress
Cardiovascular problems:
- Increased blood pressure
- Higher risk of heart attack and stroke
- Digestive disorders:
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Gastric ulcers
- Indigestion and gastroesophageal reflux
- Musculoskeletal problems:
- Muscle tension and pain
- Tension headaches and migraines
- Weakened immune system:
- Increased vulnerability to infections and illness
- Delayed wound healing
- Dermatological problems:
- Eczema and psoriasis
- Acne and other skin conditions
- Psychological Effects of Stress
1.Anxiety and depression:
- Persistent feelings of fear and worry
- Loss of interest in pleasurable activities
- Sleep disorders:
- Insomnia and difficulty falling asleep
- Non-restorative sleep and nightmares
- Cognitive problems:
- Difficulty concentrating and memory issues
- Impulsive decisions and negative thinking
- Emotional problems:
- Irritability and mood swings
- Feelings of being overwhelmed and helpless
- Unhealthy behaviors:
- Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and drug use
- Unhealthy eating habits and physical inactivity
How Can Stress Be Treated?
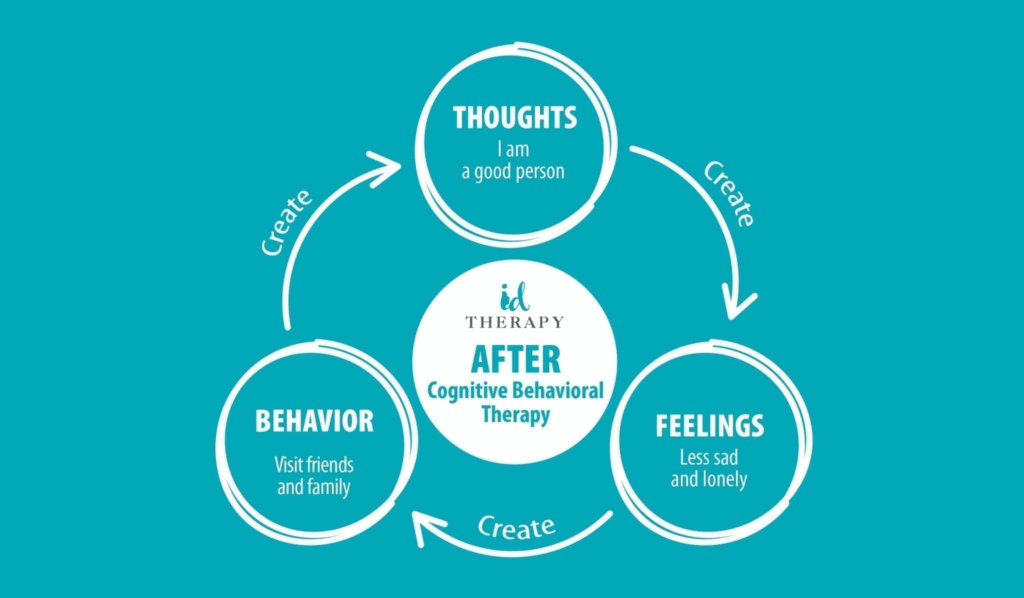



- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Description: CBT is a form of therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thinking patterns and behaviors associated with stress. Example: A person experiencing work-related performance stress may work with a CBT therapist to develop strategies for managing negative thoughts and increasing self-confidence.
- Regular Physical Exercise Regular physical activity helps release endorphins—hormones that improve mood and reduce stress. Example: A person who feels daily stress may start running three times a week, noticing a significant reduction in stress levels and an improvement in overall well-being.
- Relaxation and Mindfulness Techniques Relaxation practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing help calm the mind and reduce tension. Example: A person experiencing chronic stress may begin practicing daily meditation, using guided meditation apps to relax and reduce stress.
- Social Support Discussing problems with friends, family, or support groups can provide a sense of belonging and understanding. Example: A person going through a stressful period may join a local support group to share experiences and receive advice and emotional support.
- Time Management Efficient time organization and task prioritization can reduce stress associated with overload and deadlines. Example: A student stressed by a heavy workload may start using a planner to better organize and manage time, thus reducing academic stress.
- Psychological Counseling Discussions with a counselor or psychologist can help identify and address the underlying causes of stress. Example: A person suffering from post-traumatic stress may begin counseling sessions to work through trauma and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
- Hobbies and Recreational Activities Engaging in activities that bring pleasure and relaxation can help reduce stress. Example: A person overwhelmed by work stress may start painting or playing a musical instrument in their free time to relax and regain balance.
What Stress Prevention Methods Can You Apply?
-
Organization and Time Management
Efficient planning of daily activities helps reduce feelings of overwhelm and avoid overexertion. Use planners, calendars, and planning apps to set priorities and allocate time for each task.
Example: A busy professional may dedicate the first 30 minutes of each day to planning tasks, avoiding workload accumulation and unrealistic deadlines. -
Regular Physical Exercise
Regular physical activity improves physical health and reduces psychological tension. Include exercise in your daily routine, whether walking, running, swimming, yoga, or gym workouts.
Example: An office worker may take short 10-minute walking breaks or dedicate 30 minutes at the end of the day to exercise. -
Relaxation and Mindfulness Practices
Relaxation techniques help reduce stress and improve emotional balance. You can practice yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and other mindfulness techniques daily.
Example: A person may dedicate 10–15 minutes in the morning or evening to meditation using mindfulness apps or online guides. -
Healthy Nutrition
A balanced and healthy diet helps maintain energy and a positive mood, preventing stress. Consume nutrient-rich foods and avoid excessive sugar, caffeine, and processed foods.
Example: A person may begin including more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in their daily diet. -
Social Support
Healthy relationships and social support are essential for stress prevention. Maintain connections with friends and family and participate in social and community activities.
Example: A person may schedule regular meetings with friends or family and engage in enjoyable social activities. -
Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for physical and mental recovery and stress prevention. Establish a regular sleep routine, create a sleep-friendly environment (quiet, dark, comfortable), and avoid electronic devices before bedtime.
Example: A person who goes to bed and wakes up at the same time daily, using relaxation techniques such as reading or a warm bath, achieves better sleep quality. -
Healthy Boundaries
Setting boundaries in personal and professional life prevents overload and stress. Learn to say “no” when necessary and delegate tasks when possible.
Example: An employee may discuss workload with their supervisor and set clear boundaries regarding work hours and availability.
Can You Test Yourself to See If You Are Stressed?


How Does a Stress Test Work?
Common Types of Stress Tests
-
Self-assessment questionnaires and scales
These tools include questions about daily experiences, emotional states, and physical symptoms. A common questionnaire, such as the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), asks how often you felt stressed in recent months on a scale from 0 (never) to 4 (very often). -
Clinical evaluations
Psychologists and counselors can use structured interviews and psychological tests to assess your level of stress. A psychologist may use a clinical interview to discuss the sources of stress in your life and to evaluate their impact on your mental and physical health. -
Physiological tests
These tests measure the body’s physical responses to stress, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and levels of stress hormones (such as cortisol). A heart rate monitoring test can reveal variations in your heart rhythm during periods of rest and stress, indicating your level of physiological stress. -
Online tests and mobile applications
There are numerous online tests and mobile applications that offer quick questionnaires to assess stress. A stress management app may provide a daily test that asks about your emotional state, energy level, and physical symptoms, offering a daily stress score.
What Do Stress Tests Measure?
Physical symptoms: headaches, muscle tension, digestive issues, sleep disturbances
Emotional symptoms: anxiety, irritability, sadness, feeling overwhelmed
Behaviors: appetite changes, substance abuse, avoidance of responsibilities, concentration difficulties
Life factors: recent life events, work demands, personal relationships, work–life balance
Stress tests help identify stress levels and guide appropriate management solutions.
How Can ID Therapy Clinic Help You Overcome Stress?
Stress is a common issue in modern society, and its effective management is essential for maintaining health and overall well-being. ID Therapy Clinic offers a wide range of personalized services and treatments designed to help patients overcome stress and regain their inner balance. Below are some of the ways in which ID Therapy Clinic can help you:
Personalized Assessment and Diagnosis
One of the first steps in managing stress is identifying its causes and understanding its impact on your health. At ID Therapy Clinic, mental health specialists conduct comprehensive assessments to determine stress levels and the specific contributing factors for each patient. This personalized diagnosis allows for the development of an appropriate and effective treatment plan.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is one of the most effective methods for treating stress. ID Therapy Clinic offers CBT sessions that help you identify and modify negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to stress. Through specific techniques, you will learn how to better manage stressful situations and improve your emotional response.
Relaxation and Mindfulness Techniques
Practices such as mindfulness and meditation are integrated into the treatment programs offered by ID Therapy Clinic. These techniques help calm the mind, focus attention on the present moment, and reduce anxiety. Breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation are also part of the therapy, helping to reduce both physical and mental tension.
Individual and Group Counseling
ID Therapy Clinic provides individual counseling sessions, where you can openly discuss your concerns and worries with a specialist. Group counseling is also beneficial, offering community support and the opportunity to share experiences with others facing similar challenges. This exchange of perspectives can be extremely comforting and motivating.
Psychoeducational Interventions
Education about stress and effective stress management strategies is a key component of treatment at ID Therapy Clinic. You will learn about the mechanisms of stress, how it affects the body and mind, and discover practical techniques to control it effectively. This information empowers you to take control of your own mental health.
Ongoing Monitoring and Support
Stress management is an ongoing process, and ID Therapy Clinic provides long-term monitoring and support. Specialists will help you track your progress, adjust the treatment plan when necessary, and offer the support you need to stay on the right path.
In conclusion, stress is a natural response of the body to challenges or pressures, with the potential to affect both physical and mental health. Understanding the causes, symptoms, types, treatment options, and prevention methods of stress is crucial for managing it effectively in everyday life, thereby promoting well-being and balance in both personal and professional life.
Experience advanced neuromodulation
Free yourself from stress and anxiety – breathing exercises
WhatsApp: +40 770 942 836
Adresa: Street Strada Naum Ramniceanu, nr. 23, ap. 1,
Sector 1, Bucharest, Romania
